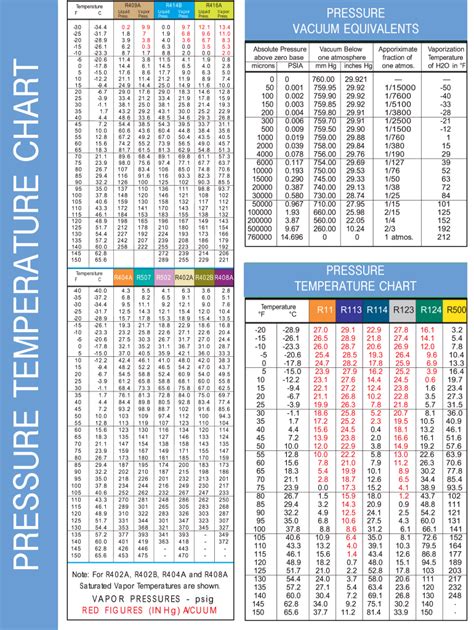
Have you ever been out in the field, sun beating down, trying to diagnose a finicky HVAC system, and your phone battery dies just as you need to check a crucial pressure-temperature reading? Or maybe you're a student, poring over textbooks, trying to grasp the fundamental relationship between pressure and temperature in refrigerants, feeling like you’re trying to decipher ancient hieroglyphs? I’ve been there. More times than I care to admit, actually. I remember one particularly sweltering summer, early in my career, staring at a blank phone screen on a commercial rooftop, utterly stranded without my digital PT chart. That day taught me a valuable lesson: technology is great, but sometimes, the old-fashioned, reliable, *printable refrigerant PT chart* is an absolute lifesaver. It’s a simple piece of paper, yet it holds the key to diagnosing, charging, and understanding the very heart of any refrigeration or air conditioning system.
This isn't just about a static chart; it's about empowerment. It's about having the critical data you need, right at your fingertips, regardless of Wi-Fi signals or battery life. It's about transforming complex thermodynamic principles into an easily digestible format that even a beginner can grasp, and an expert can rely on for rapid, accurate diagnostics. We’re going to dive deep into why these charts are indispensable, how to use them like a pro, and even how to make them your own personalized, field-ready reference. From the fundamental science to advanced troubleshooting techniques, and from choosing the right chart to keeping it durable in the toughest conditions, this comprehensive guide will equip you with everything you need to master the *printable refrigerant PT chart*. Trust me, understanding and utilizing this tool effectively will not only make your job easier but will also elevate your expertise and confidence in the field. So, let’s embark on this journey to unlock the full potential of your trusty printable PT chart – because precision starts here.
---
Table of Contents
- [The Unsung Hero: Why Every HVAC Tech Needs a Printable PT Chart](#the-unsung-hero-why-every-hvac-tech-needs-a-printable-pt-chart)
- [Decoding the Numbers: A Beginner's Guide to Reading Your PT Chart](#decoding-the-numbers-a-beginners-guide-to-reading-your-pt-chart)
- [The Refrigerant Roster: Specific Charts for Common HVAC Gases](#the-refrigerant-roster-specific-charts-for-common-hvac-gases)
- [Digital vs. Tangible: When a Printable Chart Trumps the App](#digital-vs-tangible-when-a-printable-chart-trumps-the-app)
- [Beyond the Basics: Advanced PT Chart Strategies for Seasoned Pros](#beyond-the-basics-advanced-pt-chart-strategies-for-seasoned-pros)
- [Your Go-To Chart: Tips for Printing, Laminating, and Field Durability](#your-go-to-chart-tips-for-printing-laminating-and-field-durability)
- [Troubleshooting Tales: Solving Real-World Problems with Your PT Chart](#troubleshooting-tales-solving-real-world-problems-with-your-pt-chart)
- [Evolving Refrigerants: Staying Current with Your Printable PT Charts](#evolving-refrigerants-staying-current-with-your-printable-pt-charts)
- [The DIYer's Companion: Safe & Smart Use of PT Charts for Homeowners](#the-diyers-companion-safe--smart-use-of-pt-charts-for-homeowners)
- [Customizing Your Chart: Tailoring Data for Specific Job Needs](#customizing-your-chart-tailoring-data-for-specific-job-needs)
- [How to Choose the Best Printable Refrigerant PT Chart for Your Needs](#how-to-choose-the-best-printable-refrigerant-pt-chart-for-your-needs)
- [Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Using Your PT Chart](#common-pitfalls-to-avoid-when-using-your-pt-chart)
- [Advanced Tips for Experts: Maximizing Your PT Chart's Potential](#advanced-tips-for-experts-maximizing-your-pt-charts-potential)
- [Conclusion](#conclusion)
---
The Unsung Hero: Why Every HVAC Tech Needs a Printable PT Chart

Think of the *printable refrigerant PT chart* as your thermodynamic compass in the vast wilderness of HVAC systems. It's not flashy, it doesn't make beeps or boops, but it's arguably one of the most fundamental and reliable tools in any technician's arsenal. In a world increasingly dominated by smart devices and digital apps, the humble paper chart retains a special, almost sacred, place in our toolkits. It's the steadfast companion that never runs out of battery, doesn't glare in the sun, and can be retrieved from a greasy toolbox with surprising resilience.
Here’s why this seemingly simple piece of paper is an absolute game-changer and why I firmly believe every professional, and even serious DIYer, should have one (or several):
1. Instant, Reliable Data Access: No waiting for apps to load, no searching through menus. It’s just there, open and ready. I can't tell you how many times this quick glance has saved me precious minutes on a job.
2. Battery-Proof Operation: This is huge. In the middle of a long day, or on an emergency call in a remote location, a dead phone or tablet can be a nightmare. A paper chart *always* works.
3. Durability in Harsh Environments: Printable charts, especially if laminated, can withstand dirt, grease, sweat, and even a light drizzle that would send most electronics packing. I've had laminated charts survive falls and spills that would cripple a smartphone.
4. A Foundation for Learning: For newcomers to the HVAC field, a physical chart helps solidify the understanding of refrigerant properties more tangibly than an app. You can trace lines with your finger, make notes, and really *feel* the relationships.
5. Offline Capability (Obviously!): While apps often require an internet connection for updates or specific features, your physical chart is always available, even in basements, attics, or rural areas with no signal.
6. A Backup for Digital Tools: Even if you rely heavily on digital PT apps, a *printable refrigerant PT chart* is the ultimate backup. It’s like having a spare tire – you hope you don’t need it, but you're profoundly grateful when you do.
7. Enhanced Focus: Without the distractions of notifications or other app functions, a paper chart encourages focused attention on the task at hand: reading pressures and temperatures accurately.
8. Cost-Effective: Printing a chart is virtually free if you have a printer. Compare that to the cost of a specialized app or a new smartphone!
9. Universal Compatibility: Works with *any* manifold gauge set, *any* thermometer, and *any* technician, regardless of their tech proficiency.
10. A Symbol of Preparedness: Pulling out a well-maintained, laminated PT chart subtly communicates professionalism and preparedness to your clients. It shows you're equipped for anything.
11. My Personal Scenario: I once had a client who was skeptical of my diagnosis on their old R-22 system. When I pulled out my dog-eared, but perfectly clear, *printable refrigerant PT chart* and showed them exactly how the low pressure correlated to the freezing evaporator coil, their skepticism melted away. It wasn't just data; it was tangible proof.
12. Another Scenario: During a particularly challenging rooftop unit installation, a new apprentice was struggling to visualize the superheat calculation. I handed him my laminated chart, and we physically marked the points. Seeing it laid out on paper, rather than just on a screen, helped him grasp the concept almost instantly.
Decoding the Numbers: A Beginner's Guide to Reading Your PT Chart

Alright, let's get down to brass tacks. You've got your *printable refrigerant PT chart* in hand. Now what? For the uninitiated, it might look like a jumble of numbers, but I promise, it's incredibly straightforward once you understand the basic logic. Think of it as a secret decoder ring for your HVAC system. The core principle is that for any given refrigerant, there's a precise relationship between its pressure and its temperature at saturation (the point where it's changing phase between liquid and gas).
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you read and understand your PT chart:
1. Identify the Refrigerant: First and foremost, make sure you're looking at the chart for the *correct refrigerant*. An R-410A chart won't help you diagnose an R-22 system, and vice-versa. This is probably the most common rookie mistake, and one I almost made myself on a confusingly labeled unit!
2. Understand the Columns: Most *printable refrigerant PT charts* will have at least two main columns: one for pressure (usually in PSIG – Pounds per Square Inch Gauge) and one for temperature (usually in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius). Sometimes you'll find separate columns for saturated suction (evaporator) and saturated liquid (condenser) temperatures/pressures.
3. Pressure Readings: You'll typically get pressure readings from your manifold gauges. These are your starting points. The low-side gauge measures suction pressure (evaporator), and the high-side gauge measures discharge pressure (condenser).
4. Temperature Readings: You'll use a thermometer (either clamp-on or probe) to measure the temperature of the refrigerant lines.
5. The Saturation Point: This is the magic. The PT chart primarily shows you the *saturation temperature* for a given *saturation pressure*. This is the temperature at which the refrigerant is boiling (evaporating) or condensing.
- Evaporator (Low Side): Find your suction pressure on the chart. The corresponding temperature is the *saturated suction temperature* (SST) or *evaporator temperature*. This is the temperature at which the refrigerant is boiling inside the evaporator coil.
- Condenser (High Side): Find your discharge pressure on the chart. The corresponding temperature is the *saturated condensing temperature* (SCT) or *condenser temperature*. This is the temperature at which the refrigerant is condensing inside the condenser coil.
6. Interpolation: Sometimes your exact pressure reading won't be on the chart. You'll need to "interpolate" – estimate the temperature between two listed values. For instance, if 70 PSIG is 40°F and 75 PSIG is 42°F, then 72.5 PSIG would be approximately 41°F. Don't sweat minor inaccuracies; consistency is key.
7. Superheat and Subcooling (Intro): While we'll dive deeper later, the PT chart is crucial for calculating these.
- Superheat: The difference between the actual suction line temperature (measured with your thermometer) and the saturated suction temperature (from your chart).
- Subcooling: The difference between the saturated condensing temperature (from your chart) and the actual liquid line temperature (measured with your thermometer).
8. Example Scenario: Let's say you're working on an R-410A system. Your low-side gauge reads 120 PSIG. You look at your R-410A *printable refrigerant PT chart* and find that 120 PSIG corresponds to approximately 40°F. This tells you the refrigerant in the evaporator coil is boiling at 40°F. If your actual suction line temperature is 50°F, you have 10°F of superheat. Easy, right?
9. Another Example: On the high side of that same R-410A system, your gauge reads 350 PSIG. Your chart shows that 350 PSIG for R-410A is about 105°F. This is your saturated condensing temperature. If your liquid line temperature (after the condenser) is 95°F, you have 10°F of subcooling.
10. Visual Cues: Some charts use color coding for different refrigerants or temperature ranges, which can be a great visual aid, especially for quick identification.
11. Units, Units, Units! Always double-check the units on your gauges and your chart. PSIG vs. PSI absolute, Fahrenheit vs. Celsius – mixing these up is a sure path to a misdiagnosis. My personal preference for charts is to have both F and C options if possible, just for those international units jobs.
12. Consistency: The most important thing is to be consistent in how you read and apply the chart data. Practice makes perfect, and soon you'll be reading these charts almost instinctively.
The Refrigerant Roster: Specific Charts for Common HVAC Gases
Just as different cars run on different types of fuel, various HVAC systems operate with different refrigerants. Each refrigerant has its unique pressure-temperature characteristics, which means a dedicated *printable refrigerant PT chart* is essential for each type. Using the wrong chart is akin to trying to read a map of New York City while standing in Los Angeles – utterly useless and potentially misleading. Let's delve into some of the most common refrigerants you'll encounter and why their specific charts are vital.
Here's a breakdown of common refrigerants and what to look for on their respective charts:
1. R-22 (Chlorodifluoromethane): The Legacy Refrigerant
- Context: Once the industry standard, R-22 is an HCFC (hydrochlorofluorocarbon) that is being phased out due to its ozone-depleting potential. You'll still find it in older systems, especially residential ones.
- Chart Characteristics: Typically has a distinct pressure range, often lower than modern refrigerants like R-410A. Its saturation temperatures for a given pressure will be unique.
- Why it's Crucial: Servicing an R-22 system *requires* an R-22 chart. Guessing pressures will lead to incorrect charging and potential system damage.
- Personal Scenario: I recall a frantic call about an old R-22 unit that wasn't cooling. The previous tech had tried to charge it using an R-410A chart, leading to massive overcharging and dangerously high pressures. A quick check with the correct R-22 printable chart immediately revealed the error.
2. R-410A (Puron/Genset): The Modern Workhorse
- Context: An HFC (hydrofluorocarbon) blend, R-410A became the primary replacement for R-22 in new residential and light commercial equipment. It operates at significantly higher pressures than R-22.
- Chart Characteristics: You'll notice much higher pressure values for corresponding temperatures compared to R-22. It's a "zeotropic" blend, but it behaves almost like an azeotropic blend, meaning it has a very small "temperature glide" during phase change, making its PT chart relatively straightforward.
- Why it's Crucial: Due to its high pressures, using an R-22 chart on an R-410A system is a recipe for disaster. Always verify.
- Tip: When looking for a *printable refrigerant pt chart*, R-410A is one you absolutely must have if you work on modern residential HVAC.
3. R-134a (Tetrafluoroethane): Automotive & Commercial Refrigeration
- Context: Another HFC, R-134a is widely used in automotive air conditioning, medium-temperature commercial refrigeration (e.g., supermarket display cases), and some chillers.
- Chart Characteristics: Pressures are generally lower than R-410A, making it suitable for different applications.
- Why it's Crucial: Its unique properties mean its chart is distinct from R-22 or R-410A. Cross-referencing is not an option.
4. R-32 (Difluoromethane): The Next Generation
- Context: R-32 is a single-component HFC refrigerant with a lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) than R-410A. It's gaining popularity, especially in mini-split and VRF systems, as the industry moves towards more environmentally friendly options.
- Chart Characteristics: Operates at similar pressures to R-410A but has different thermodynamic properties.
- Why it's Crucial: As R-32 systems become more prevalent, having its dedicated *printable refrigerant PT chart* is becoming essential for staying current.
5. R-404A / R-507 (Blends): Low-Temperature Refrigeration
- Context: Common in low-temperature refrigeration applications (e.g., freezers). R-404A is an HFC blend, and R-507 is an azeotropic blend. Both are high-GWP and are being phased down.
- Chart Characteristics: These charts will reflect properties suitable for much colder evaporative temperatures.
- Why it's Crucial: Critical for accurate charging and troubleshooting of commercial freezers and cold rooms.
6. R-407C (Blend): R-22 Replacement Alternative
- Context: An HFC blend that was developed as a retrofit option for R-22 systems. It has a notable "temperature glide."
- Chart Characteristics: Its chart might indicate two temperatures for a given pressure (bubble point and dew point) due to its glide, which can be a bit more complex to interpret for beginners.
- Why it's Crucial: Understanding glide is key here. For R-407C, you often use the dew point for superheat and bubble point for subcooling.
7. R-448A / R-449A (Low GWP Blends): Newer Commercial Options
- Context: These HFO/HFC blends are designed as replacements for R-404A/R-507 in commercial refrigeration, offering significantly lower GWP.
- Chart Characteristics: Like R-407C, they are blends and may exhibit temperature glide, requiring careful interpretation of bubble and dew points.
- Why it's Crucial: As older refrigerants are phased down, these charts will become more common for commercial refrigeration technicians.
8. R-1234yf (HFO): Automotive AC & Chillers
- Context: An HFO (hydrofluoroolefin) with an extremely low GWP, making it a sustainable choice for automotive AC and increasingly in some chiller applications.
- Chart Characteristics: Unique pressure-temperature relationships, distinct from HFCs.
- Why it's Crucial: Essential for automotive technicians working on newer vehicles, and for some commercial chiller applications.
9. Ammonia (R-717): Industrial Refrigeration
- Context: A natural refrigerant with excellent thermodynamic properties and zero ODP/GWP, but highly toxic and flammable. Used primarily in large industrial refrigeration plants.
- Chart Characteristics: Very different pressure and temperature ranges compared to synthetic refrigerants.
- Why it's Crucial: Specialized industrial applications demand precise ammonia PT charts for safety and efficiency.
10. Propane (R-290) / Isobutane (R-600a): Natural Hydrocarbons
- Context: Natural refrigerants with very low GWP, used in small commercial refrigeration (e.g., beverage coolers) and increasingly in residential applications outside the US. Highly flammable.
- Chart Characteristics: Distinct pressures and temperatures, similar to R-22 in some respects but for different applications.
- Why it's Crucial: As natural refrigerants gain traction, having these charts becomes important for specific niche equipment.
11. CO2 (R-744): Transcritical Systems
- Context: Carbon Dioxide, another natural refrigerant, is used in transcritical systems, especially in supermarkets. Operates at extremely high pressures.
- Chart Characteristics: Charts will show very high pressures, often extending into the transcritical region where traditional PT chart logic shifts.
- Why it's Crucial: This is a highly specialized area, and the CO2 PT chart is fundamentally different due to its transcritical operation.
When you're searching for a *printable refrigerant PT chart*, always prioritize accuracy and ensure it's specifically for the refrigerant you're working with. A multi-refrigerant chart can be handy, but ensure it clearly delineates each refrigerant's data.
Digital vs. Tangible: When a Printable Chart Trumps the App
In today's hyper-connected world, it's easy to assume that a digital app on your smartphone or tablet is always the superior tool. And while digital PT chart apps offer fantastic features like automatic superheat/subcooling calculations, refrigerant identification, and even data logging, there are specific scenarios where a good old-fashioned *printable refrigerant PT chart* isn't just a viable alternative – it's the *superior* choice. This isn't about being anti-tech; it's about being pragmatic and understanding the right tool for the right job.
Here are the situations where a tangible, printable chart truly shines:
1. Extreme Temperatures:
- Scenario: You're working in the scorching summer heat on a rooftop, or in a freezing walk-in freezer. Extreme temperatures can cause touchscreens to become unresponsive, batteries to drain rapidly, or even damage the device itself.
- Why Printable Wins: A laminated chart doesn't care if it's 110°F or -20°F. It works flawlessly. I've had phones literally shut down in extreme heat, leaving me scrambling until I remembered my backup paper chart.
2. Wet or Dirty Environments:
- Scenario: You're in a damp crawl space, a leaky mechanical room, or simply have greasy hands from working on equipment.
- Why Printable Wins: A laminated *printable refrigerant PT chart* can be wiped clean. A smartphone can be ruined by a single drop of water or a smear of oil. Even "ruggedized" phones have their limits.
3. Battery Life Concerns:
- Scenario: Long service calls, multiple jobs back-to-back, or forgotten chargers. Your phone is your communication device, camera, and navigation tool – do you really want it dying on you because you're using it as a PT chart?
- Why Printable Wins: Infinite battery life. Period. My go-to strategy is to save my phone battery for communication and critical documentation, while the chart handles the thermodynamics.
4. Signal Blackouts and Remote Locations:
- Scenario: Deep within a building, in a remote rural area, or underground, cellular data and Wi-Fi signals can be nonexistent. Many advanced app features require connectivity.
- Why Printable Wins: It’s completely independent of any network. Your data is always available, a constant in an unpredictable world.
5. Training and Learning:
- Scenario: You're teaching an apprentice, or you're a student trying to grasp the fundamental concepts.
- Why Printable Wins: A physical chart allows for tactile interaction. You can point, trace with your finger, make notes, and visually connect pressure points to temperature values in a way that feels more concrete than a digital interface. I personally learned the most by physically drawing on my first *printable refrigerant PT chart*.
6. Quick Reference and "Dashboard" View:
- Scenario: You're taking multiple readings and need to quickly cross-reference various pressures and temperatures without navigating through an app.
- Why Printable Wins: You can lay it out, highlight common values, or even have multiple charts side-by-side. It’s an instant, comprehensive overview without toggling screens.
7. Cost and Accessibility:
- Scenario: You're on a tight budget, or you don't have access to a smartphone or tablet.
- Why Printable Wins: Printing a chart costs pennies. It democratizes access to critical information, ensuring everyone can have this essential tool.
8. Reliability and Simplicity:
- Scenario: When all else fails, or you just need a straightforward answer without any bells and whistles.
- Why Printable Wins: No software glitches, no updates needed, no user interface to learn. It’s a pure, unadulterated data source. My most memorable "win" was diagnosing a complex commercial chiller issue after my tablet crashed, purely relying on my laminated PT chart and basic math. It felt incredibly satisfying.
9. Client Confidence:
- Scenario: Explaining a diagnosis to a client who might be wary of "tech wizardry."
- Why Printable Wins: A tangible chart allows you to physically point to data and explain the science in a relatable way. It feels more transparent and professional than simply showing numbers on a screen.
10. A Personal Touch:
- Scenario: You've customized your chart with notes, frequently used values, or even a personal anecdote.
- Why Printable Wins: It becomes *your* chart, a trusted companion that has seen you through countless jobs. This personal connection is something a generic app can rarely replicate.
While digital tools certainly have their place, never underestimate the power and practicality of a well-chosen, durable *printable refrigerant PT chart*. It’s a testament to the enduring value of simple, effective engineering.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced PT Chart Strategies for Seasoned Pros

For the seasoned HVAC technician, the *printable refrigerant PT chart* is far more than just a lookup table; it's a diagnostic powerhouse. Once you've mastered the fundamentals of reading pressures and temperatures, you can leverage this simple tool for sophisticated troubleshooting, system optimization, and even predictive maintenance. This is where the chart transitions from a reference guide to a strategic partner in your diagnostic process.
Here’s how advanced users can unlock the full potential of their PT chart:
1. Mastering Superheat and Subcooling for Precision Charging:
- Concept: These two measurements are paramount for proper system operation. Superheat indicates if the evaporator is getting enough refrigerant, and subcooling indicates if the condenser is properly removing heat and if the liquid line is full.
- Advanced Use: Don't just calculate them; *interpret* them in conjunction with outdoor and indoor temperatures. An R-410A system might need 8-12°F superheat and 10-14°F subcooling, but these targets vary based on manufacturer specifications and ambient conditions. Your PT chart is the bedrock for these calculations.
- Personal Scenario: I once spent hours trying to balance a multi-zone system. It wasn't until I meticulously calculated superheat and subcooling for each zone using my PT chart that I realized