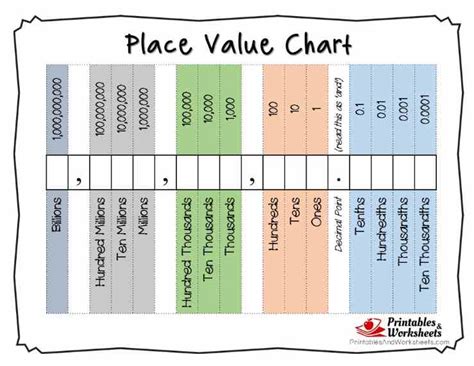
Have you ever looked at a string of numbers with a decimal point and felt a tiny flutter of panic? Or perhaps you're a parent, a teacher, or a tutor, watching a bright-eyed learner grapple with the seemingly abstract concept of decimals, their frustration growing with each misplaced digit. Trust me, I’ve been there. I remember my own struggle in elementary school, staring blankly at a page of decimal problems, feeling like I was trying to understand a secret code without the key. Then, one day, my brilliant fifth-grade teacher introduced us to a simple, yet profoundly powerful, tool: the place value chart. It was like a light switch flipped on in my brain, transforming confusion into clarity. And when she handed us a *printable* version to keep, suddenly, decimals weren't just numbers on a page; they were concrete, understandable building blocks.
That "aha!" moment is precisely what I want to help you achieve today. We're diving deep into the world of the place value chart printable decimals – not just what they are, but *why* they are indispensable, how to use them, where to find the best ones, and how to integrate them into a learning journey that fosters true understanding and confidence. This isn't just about memorizing positions; it's about building a foundational understanding that will serve you or your learners for a lifetime, from balancing a budget to tackling advanced scientific notation. If you're ready to transform decimal dread into decimal mastery, you've come to the right place. Let's unlock the magic together!
---
Table of Contents

- [The Unsung Heroes: What Exactly Are Place Value Charts?](#the-unsung-heroes-what-exactly-are-place-value-charts)
- [Unlocking Decimal Mysteries: Why Place Value Charts Are Non-Negotiable](#unlocking-decimal-mysteries-why-place-value-charts-are-non-negotiable)
- [Your Perfect Partner: Designing and Customizing Your Printable Decimal Chart](#your-perfect-partner-designing-and-customizing-your-printable-decimal-chart)
- [From Zero to Hero: Step-by-Step Guide to Using Your Printable Chart for Decimals](#from-zero-to-hero-step-by-step-guide-to-using-your-printable-chart-for-decimals)
- [Beyond the Basics: Advanced Decimal Concepts with Your Chart](#beyond-the-basics-advanced-decimal-concepts-with-your-chart)
- [The Educator's Toolkit: Innovative Teaching Strategies with Place Value Charts](#the-educators-toolkit-innovative-teaching-strategies-with-place-value-charts)
- [Common Roadblocks & How to Navigate Them](#common-roadblocks--how-to-navigate-them)
- [Integrating Place Value into Everyday Life & Beyond the Classroom](#integrating-place-value-into-everyday-life--beyond-the-classroom)
- [The Digital Age & Printables: Finding, Creating, and Utilizing Online Resources](#the-digital-age--printables-finding-creating-and-utilizing-online-resources)
- [How to Choose the Best Place Value Chart Printable for Your Needs](#how-to-choose-the-best-place-value-chart-printable-for-your-needs)
- [Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Using Place Value Charts](#common-pitfalls-to-avoid-when-using-place-value-charts)
- [Advanced Tips for Mastering Decimal Place Value](#advanced-tips-for-mastering-decimal-place-value)
- [Conclusion](#conclusion)
---
The Unsung Heroes: What Exactly Are Place Value Charts?
Before we dive into the decimal delights, let's establish a solid foundation. At its heart, a place value chart is a visual organizer that helps us understand the value of each digit in a number based on its position. It’s the backbone of our base-10 number system, and honestly, it’s one of the most underrated tools in elementary math education.
### Understanding the Core Concept
1. Digits and Value: Every number is made up of digits (0-9). The *value* of a digit isn't just the digit itself, but also where it sits within the number. For example, the '2' in '20' means twenty, but the '2' in '200' means two hundred. The chart makes this explicit.
2. The Power of Ten: Our number system is built on powers of ten. Moving one place to the left multiplies the value by ten; moving one place to the right divides it by ten. This simple rule governs everything.
3. Whole Number Refresher:
- Ones Place: The rightmost digit before the decimal point (implied if not present). It represents single units.
- Tens Place: To the left of the ones, representing groups of ten.
- Hundreds Place: To the left of the tens, representing groups of one hundred.
- ...and so on, extending infinitely to the left (thousands, ten thousands, hundred thousands, millions, etc.).
4. The Pivotal Decimal Point: This tiny dot is the anchor! It clearly separates the whole number part from the fractional (decimal) part. It always sits *between* the ones place and the tenths place.
5. Introducing Decimal Places:
- Tenths Place: The first digit *after* the decimal point. It represents parts of ten (e.g., 0.1 is one-tenth).
- Hundredths Place: The second digit after the decimal point. It represents parts of one hundred (e.g., 0.01 is one-hundredth).
- Thousandths Place: The third digit after the decimal point. It represents parts of one thousand (e.g., 0.001 is one-thousandth).
- ...and so on, extending infinitely to the right (ten-thousandths, hundred-thousandths, millionths, etc.).
6. Symmetry Around the Ones: Notice the beautiful symmetry? Tens and tenths, hundreds and hundredths, thousands and thousandths. The "th" ending always signals a fractional part, less than one. This was a revelation for me when I first saw it visually.
7. Reading Decimals Aloud: The chart helps immensely with this. You read the whole number part, then say "and" for the decimal point, then read the decimal part as if it were a whole number, followed by the name of the place value of its last digit. (e.g., 3.14 is "three AND fourteen hundredths").
8. Visualizing Magnitude: A well-designed place value chart printable decimals version makes it easy to see that 0.5 is much larger than 0.05, even though both have a '5'.
9. Laying the Groundwork for Operations: Understanding place value is foundational for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing decimals. Without it, these operations become rote memorization, prone to errors.
10. Bridge to Fractions: Decimals are just another way to write fractions. A place value chart helps show this equivalency (e.g., 0.7 = 7/10, 0.25 = 25/100).
11. My Experience: I vividly remember a student who mixed up 0.1 and 0.01 constantly. Once we used a large, laminated chart and physically placed number tiles into the 'tenths' and 'hundredths' columns, the lightbulb moment was immediate and permanent. It’s incredible how a visual aid can cement a concept.
12. Foundation for Scientific Notation: While advanced, the concept of powers of ten and moving the decimal point (which place value charts reinforce) is crucial for understanding scientific notation later on.
Unlocking Decimal Mysteries: Why Place Value Charts Are Non-Negotiable

Okay, so we know what they are. But in an age of digital calculators and instant answers, why bother with a humble place value chart printable decimals tool? The answer lies in deep understanding over superficial calculation. These charts are not just aids; they are gateways to true mathematical literacy.
### The Indispensable Benefits
1. Concrete Visualization: Abstract numbers become tangible. Instead of just seeing "0.75," a chart allows you to see "0 ones, 7 tenths, and 5 hundredths." This visual mapping is critical for learners who are still developing abstract reasoning skills.
2. Demystifying the Decimal Point: For many, the decimal point is a magical barrier. The chart clearly defines its role as the separator between whole numbers and parts of a whole, reducing its intimidating aura.
3. Preventing Misconceptions:
- "Longer is Larger": This common error (e.g., thinking 0.123 is larger than 0.4 because it has more digits) is directly tackled by comparing digits in their respective places. My own child, a few years ago, swore that 0.9 was smaller than 0.10 because "ten is bigger than nine." A quick session with the chart, filling in a zero for 0.9 (0.90) made it click.
- Misplacing Zeros: Understanding that 0.5, 0.50, and 0.500 are equivalent becomes clear when you see the zeros filling empty place values to the right without changing the initial value.
4. Aids in Reading and Writing Decimals: As discussed, the chart provides a clear framework for correctly naming decimal numbers, which is often a stumbling block. It ensures you read "0.34" as "thirty-four hundredths," not "zero point three four."
5. Supports Decimal Operations:
- Addition/Subtraction: Lining up the decimal points becomes intuitive when you're aligning digits in their correct place value columns.
- Multiplication/Division: While more complex, the chart helps in estimating answers and understanding the magnitude shifts involved.
6. Builds Number Sense: It helps students develop an intuitive feel for the size and relationship of numbers, even when they involve fractions of a whole. This is the bedrock of mathematical fluency.
7. Self-Correction Tool: Learners can use the chart independently to check their work, identify where they went wrong, and correct their own mistakes. This fosters autonomy.
8. Versatility for Different Learners:
- Visual Learners: Absolutely thrive with the clear layout and color-coding.
- Kinesthetic Learners: Can manipulate number tiles or dry-erase markers on a laminated chart.
- Auditory Learners: Benefit from hearing the place names as they interact with the chart.
9. Reduces Math Anxiety: When a concept clicks, and a tool helps you understand, anxiety dissipates. The chart provides a structured, predictable way to approach decimals, making them less daunting.
10. A "Take-Home" Resource: The beauty of a place value chart printable decimals version is its accessibility. Print it, laminate it, stick it on the fridge – it’s a constant, personal reference tool that reinforces learning outside the classroom.
11. Cost-Effective and Readily Available: Unlike expensive manipulatives, a printable chart is just a click and a print away, making it an equitable learning resource for everyone.
12. My Personal Scenario: As a tutor, I once had a student who was convinced that decimals were "magic numbers" that defied logic. We spent an entire session just *playing* with a large printable chart, moving digits around, talking about the value changes, and coloring in sections to represent tenths and hundredths. By the end, the "magic" had been replaced with logical understanding, and it was genuinely heartwarming to witness.
Your Perfect Partner: Designing and Customizing Your Printable Decimal Chart
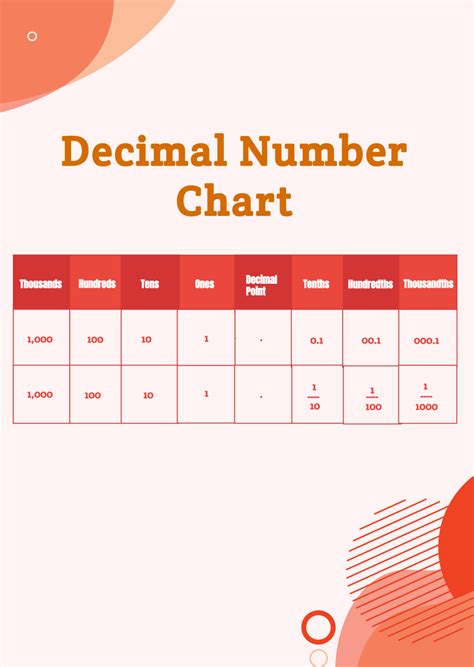
The beauty of a place value chart printable decimals tool is its adaptability. You're not stuck with a one-size-fits-all solution. You can tailor it to fit specific needs, learning styles, or even just personal aesthetic preferences. Let's explore how to make your chart truly yours.
### Creative Customization Ideas
1. Choose Your Scope:
- Basic: Ones, tenths, hundredths, thousandths. Perfect for initial introduction.
- Extended: Include tens, hundreds, thousands on the whole number side, and up to ten-thousandths or hundred-thousandths on the decimal side for more advanced work.
- Targeted: Focus solely on decimals for learners who have mastered whole numbers.
2. Color-Coding Magic:
- Whole Numbers vs. Decimals: Use a different background color for the whole number side (e.g., blue) and the decimal side (e.g., green). This clearly differentiates the two parts of a number.
- Individual Place Values: Assign a unique color to each column (e.g., yellow for ones, orange for tens, light blue for tenths, dark blue for hundredths). This helps visual learners track positions.
- My preference: I like to use warm colors for whole numbers and cool colors for decimals. It creates a nice visual distinction.
3. Labeling Options:
- Full Names: "Ones," "Tenths," "Hundredths."
- Abbreviated: "O," "T," "H," "th," "hth." (Use with caution for beginners).
- Numerical Notation: Add "10^0" for ones, "10^1" for tens, "10^-1" for tenths, etc., for older learners connecting to exponents.
4. Visual Aids within Cells:
- Base-10 Blocks: Integrate small images of base-10 blocks (units, rods, flats) into the whole number columns. For decimals, you can use grid representations (e.g., a 10x10 grid for hundredths).
- Fraction Equivalents: Add small fraction representations below the decimal place names (e.g., 1/10 below "Tenths," 1/100 below "Hundredths").
5. Size Matters:
- Desktop Size: A standard 8.5x11 inch chart for individual use.
- Large Wall Chart: Print on larger paper or piece together multiple sheets for classroom or homeschooling display. This is fantastic for group activities.
- Mini-Charts: Small versions to tape into notebooks or keep in a pencil case for quick reference.
6. Material and Durability:
- Lamination: Highly recommended for repeated use with dry-erase markers. This is a game-changer for interactive learning.
- Card Stock: Thicker paper will last longer than regular printer paper.
- Protective Sleeves: If lamination isn't an option, clear plastic sleeves work well.
7. Interactive Elements:
- Cut-out Digits: Provide separate cut-out digits (0-9) that learners can physically place into the chart's columns.
- Sliders: Create a chart with slots and paper strips that can be "slid" to represent different numbers, showing the shift in place value.
8. Personalized Themes:
- Sports Theme: "Scoreboard Place Value."
- Space Theme: "Galactic Place Values."
- Animal Theme: "Animal Kingdom Numbers."
- This adds a fun, engaging element, especially for younger learners.
9. "My Chart Story": Encourage learners to draw a small picture or write a sentence about how they used the chart on the back of their personalized printable. This makes it a personal artifact.
10. The "Zero Placeholder" Reminder: Add a small note or a distinct color for the decimal point itself, and perhaps a faded "0" in empty decimal places to reinforce that concept (e.g., 0.5 can be thought of as 0.50 or 0.500).
11. Scenario: The Homeschooling Parent: A homeschooling parent I know, whose child struggled with visual processing, created a highly tactile place value chart printable decimals version. She printed it on magnet paper, then used magnetic numbers. The child could physically move the numbers, and the "stick" of the magnets provided valuable sensory feedback. It was messy, but it worked wonders!
12. Advanced Feature: Number Line Integration: For older students, consider a chart that includes a small number line representation below or above, showing where the decimal falls between two whole numbers (e.g., 0.75 between 0 and 1).
From Zero to Hero: Step-by-Step Guide to Using Your Printable Chart for Decimals
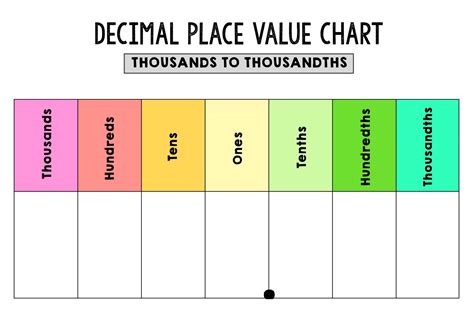
You've got your custom place value chart printable decimals ready. Now, let's put it to work! This section is all about the practical, hands-on application of the chart to truly grasp decimal concepts.
### Practical Application Techniques
1. Reading Numbers Aloud (The Foundation):
- Step 1: Place the Number. Write or place digits in the correct columns. Remember the decimal point goes *between* the ones and tenths.
- Step 2: Read the Whole Number. Read the digits to the left of the decimal point as a standard whole number.
- Step 3: Say "and" for the Decimal Point. This is crucial for distinguishing decimals from whole numbers.
- Step 4: Read the Decimal Part. Read the digits to the right of the decimal point as if they were a whole number.
- Step 5: Name the Place Value of the Last Digit. For example, if the last digit is in the hundredths column, the number ends with "hundredths."
- *Example:* For 12.345, you'd place 1 in tens, 2 in ones, decimal, 3 in tenths, 4 in hundredths, 5 in thousandths. Read as "twelve AND three hundred forty-five thousandths."
2. Writing Decimals from Words:
- Step 1: Identify the "and." This tells you where the decimal point goes. If no "and" is present, it's either a whole number or a decimal less than one (starting with 0).
- Step 2: Write the Whole Number Part. Place these digits to the left of where the decimal point will be.
- Step 3: Place the Decimal Point.
- Step 4: Identify the "Place Value" Word. This tells you how many decimal places you need (e.g., "tenths" = 1 decimal place, "hundredths" = 2, "thousandths" = 3).
- Step 5: Write the Decimal Part. Fill in the digits, ensuring the last digit lands in the identified place value. Add leading zeros after the decimal point if necessary to fill the places.
- *Example:* "Four hundred six and twenty-three thousandths." Write "406." Then, "thousandths" means 3 decimal places. "Twenty-three" needs to end in the thousandths place, so it's 0.023. Combine: 406.023.
3. Comparing Decimals:
- Step 1: Line Them Up. Place both numbers on the chart, aligning the decimal points.
- Step 2: Fill in Zeros. Add trailing zeros to the number with fewer decimal places so both numbers have the same number of digits after the decimal point (e.g., compare 0.5 to 0.45 by making 0.5 into 0.50). This is a game-changer!
- Step 3: Compare from Left to Right. Start with the largest place value (farthest left). The first digit where they differ determines which number is larger.
- *Example:* Compare 0.7 and 0.68. On the chart, 0.7 becomes 0.70. Comparing tenths: 7 is greater than 6. So, 0.7 > 0.68.
4. Rounding Decimals:
- Step 1: Identify the Rounding Place. Find the column you need to round to (e.g., "round to the nearest tenth").
- Step 2: Look to the Right. Look at the digit immediately to the right of the rounding place.
- Step 3: Apply the Rule: If that digit is 5 or greater, round up the digit in the rounding place. If it's 4 or less, keep the digit in the rounding place the same.
- Step 4: Drop the Rest. Remove all digits to the right of the rounding place.
- *Example:* Round 3.14159 to the nearest hundredth. Hundredths place has a '4'. Look to its right: '1'. Since 1 is less than 5, keep the '4' as is. Drop the '159'. Result: 3.14.
5. Converting Decimals to Fractions (and vice-versa):
- Decimal to Fraction: Place the decimal on the chart. The number of digits after the decimal tells you the denominator (e.g., 1 digit = tenths, 2 digits = hundredths). The digits themselves become the numerator. Simplify if possible.
- *Example:* 0.75. The '5' is in the hundredths place. So, it's 75/100. Simplify to 3/4.
- Fraction to Decimal: Divide the numerator by the denominator. The chart can help place the resulting digits.
6. Adding and Subtracting Decimals:
- Step 1: Line Up Decimal Points. This is the golden rule, and the chart makes it effortless.
- Step 2: Fill in Zeros. Add trailing zeros so all numbers have the same number of decimal places.
- Step 3: Add/Subtract as Usual. Perform the operation column by column, carrying or borrowing as needed.
- Step 4: Place the Decimal Point. The decimal point in the answer will be directly below the decimal points in the problem.
- *My personal scenario:* I used to make a massive version of this place value chart printable decimals on butcher paper and have students physically write numbers on sticky notes to place them. When adding, they'd see exactly why aligning by the decimal was critical. It looked messy, but it was incredibly effective.
7. Visualizing Value: Use the chart to demonstrate that 0.5 is equal to 0.50 or 0.500 by adding zeros to the right without changing the value. This helps in understanding equivalent decimals.
8. Understanding "Ths" vs. "S": Point out the "s" ending for whole number places (tens, hundreds) and the "ths" ending for decimal places (tenths, hundredths). The chart makes this visual distinction.
9. Place Value Houses: Sometimes, teachers use the analogy of "houses" for each place value. The chart provides the perfect floor plan for these houses.
10. Practice with Real-World Numbers: Use prices (e.g., $1.99), measurements (e.g., 2.5 meters), or sports statistics (e.g., a batting average of 0.305) to fill the chart. This makes it relevant.
11. Error Analysis: If a learner makes a mistake, have them place their incorrect answer on the chart next to the correct answer. The visual discrepancy often helps them pinpoint their error.
12. The "Zero Placeholder" Problem: A common error is ignoring zeros as placeholders. The chart visually highlights that 0.05 is five hundredths, not five tenths, because the zero is holding the tenths place.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Decimal Concepts with Your Chart

While the place value chart printable decimals tool is a cornerstone for foundational understanding, its utility doesn't stop there. For more seasoned learners, or those ready to push their decimal knowledge further, the chart can still be an invaluable guide for more complex operations and concepts.
### Advanced Applications and Insights
1. Multiplying Decimals (Understanding the Shift):
- Initial Concept: While you don't typically place the *product* directly on the chart during multiplication, the chart helps explain *why* the decimal point moves.
- Visualizing Magnitude: When you multiply 0.1 by 0.1, you get 0.01. The chart shows that "a tenth of a tenth" is a "hundredth," visually reinforcing the concept of smaller and smaller parts.
- Estimation: Before multiplying, use the chart to quickly round decimals to whole numbers for an estimate (e.g., 0.9 x 3.2 is approximately 1 x 3 = 3).
- *Hypothetical Scenario:* I once used a large chart to show a student multiplying 2.5 by 10. We physically slid the number '25' one place to the left, showing how 2.5 becomes 25.0, reinforcing that multiplying by 10 shifts all digits one place to the left.
2. Dividing Decimals (Reverse Shift):
- Understanding the Quotient: Similar to multiplication, the chart helps explain the shifting of the decimal point when dividing by powers of ten.
- Conceptualizing Division: When you divide a whole by a decimal (e.g., 5 ÷ 0.5), it means "how many halves are in 5?" The chart helps visualize that 0.5 is half, so there are ten halves in 5.
- My Subjective Tip: For division, I find it immensely helpful to think of it as converting to whole numbers first. If you multiply both the dividend and divisor by the same power of ten to make the divisor a whole number, the chart helps keep track of the place values as you adjust the numbers.
3. Scientific Notation Connection:
- Large Numbers: Use the chart to see how many places the decimal point moves when converting a large number like 3,450,000 to 3.45 x 10^6. Each "jump" over a place value on the chart corresponds to a power of 10.
- Small Numbers: Similarly, for numbers like 0.0000078, the chart helps count the negative powers of ten (7.8 x 10^-6).
4. Significant Figures (for Science/Engineering Students):
- Precision and Place Value: The chart can be used to identify which digits are significant based on their position and the concept of measurement precision. Leading zeros (0.005) are not significant, while trailing zeros after a decimal point (0.500) are.
- Understanding Error: In scientific measurements, the last significant digit often implies a level of uncertainty. The chart helps visualize which place value that uncertainty falls in.
5. Decimal to Percent Conversion:
- Multiplying by 100: To convert a decimal to a percentage, you multiply by 100 (move the decimal point two places to the right) and add the percent sign. The chart makes this "move" explicit.
- *Example:* 0.75 on the chart. Move decimal two places right to get 75. Then add %.
6. Decimal to Fraction (Complex):
- For repeating decimals, the chart doesn't directly convert, but it reinforces the concept that not all decimals terminate neatly in a specific place value. It helps understand *why* some fractions produce repeating decimals (e.g., 1/3 = 0.333...).
7. Understanding Irrational Numbers (Briefly):
*